Description
The HTML <div> tag is used for defining a section of your document. With the div tag, you can group large sections of HTML elements together and format them with CSS. The difference between the div tag and the span tag is that the div tag is used with block-level elements whilst the span tag is used with inline elements.
- Block-Level Element: The
<div>tag is a block-level element, meaning it takes up the full width and starts on a new line. - Styling with CSS: It can be styled using CSS, allowing customization like width, background color, padding, and margins.
- Inline-Block Option: By using
display: inline-block, a<div>can behave like an inline element while retaining block-level features. - Used for Layouts:
<div>is often used in layouts with Flexbox or Grid to organize content and arrange sections of a webpage.
<div>
<!-- all others html Code will come inside -->
</div>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* Basic styling for better readability */
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
margin: 20px;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
}
/* Styling for the div blocks */
div {
color: white;
background-color: #009900;
/* Fixed the color */
margin: 10px 0;
padding: 10px;
font-size: 20px;
border-radius: 5px;
/* Optional: Adds rounded corners */
box-shadow: 0 4px 6px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
/* Optional: Adds subtle shadow */
}
/* Headings for clarity */
h1 {
font-size: 28px;
color: #333;
}
/* Styling for the section and article */
section {
margin-top: 30px;
}
/* Responsive styling */
@media (max-width: 600px) {
div {
font-size: 18px;
padding: 8px;
}
h1 {
font-size: 24px;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<article>
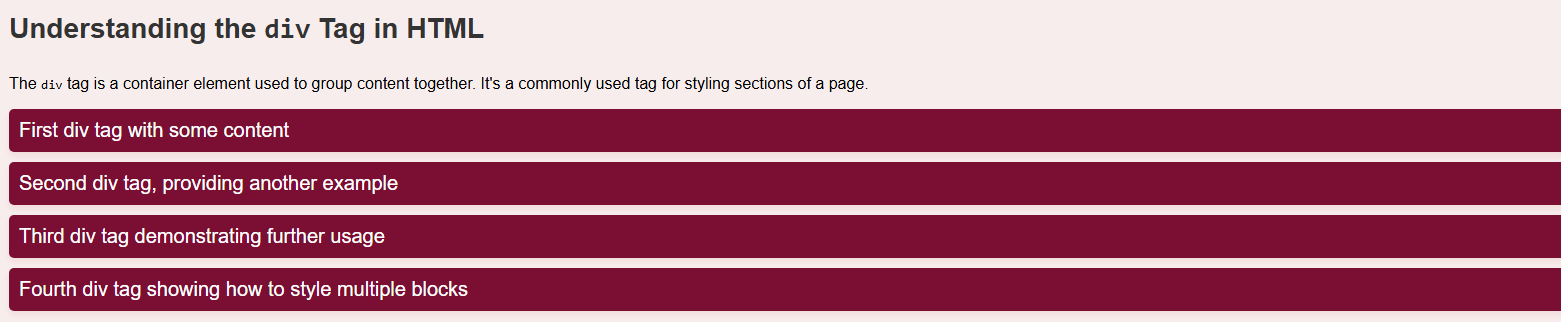
<h1>Understanding the <code>div</code> Tag in HTML</h1>
<section>
<p>The <code>div</code> tag is a container element used to group content together.
It's a commonly used tag for styling sections of a page.</p>
<div>First div tag with some content</div>
<div>Second div tag, providing another example</div>
<div>Third div tag demonstrating further usage</div>
<div>Fourth div tag showing how to style multiple blocks</div>
</section>
</article>
</body>
</html>
Output :
How to Style the div Tag
The <div> tag is easy to style and is used by developers to group content all together. It accepts almost all type of CSS properties, making it very versatile. Here’s how to style a <div> tag in a simple way:
1. Apply Font Properties with div
The <div> tag can be styled using properties like font-size, font-family,font-weight and font-style to control the appearance of text
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Font Properties Example</title>
<style>
.text-style {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif; /* Font type */
font-size: 24px; /* Font size */
font-weight: bold; /* Makes text bold */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="text-style">
This is a simple example of applying font properties to a div element.
</div>
</body>
</html>
OutPut :

Create a Shadow Effect with the Div Tag
The box-shadow property adds a shadow effect to a <div>
Code :
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Shadow Effect with div</title>
<style>
.shadow-effect {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
background-color: lightblue;
margin: 50px auto;
box-shadow: 10px 10px 20px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
padding: 20px;
font-size: 20px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="shadow-effect">
This div has a shadow effect.
</div>
</body>
</html>
OutPut :


